Today’s discussion is on Polkadot; a term I stumbled on while surfing the cryptocurrency web.
Guess your mind is showing you those circles in different colors and sizes already?… Nah, that’s far from what this is about.
Polkadot is a secure network protocol that enables interoperability among blockchains.
It seeks to create a web that is decentralized and allows you to transfer any type of data.
Yes, I noticed the unfamiliar terms but hold up, let’s not jump the gun yet…
In subsequent subheadings, I will be letting out details chronologically that will help you understand what Polkadot is all about.
Let’s get the review started already!
Polkadot Post Outline
Here, you will find a rundown of what and what I will be discussing.
The subtopics include:
- What is Polkadot?
- Why Do We Need Polkadot?
- Polkadot Development Phases
- Polkadot Technology: An Insight On How It Works
- DOT – Polkadot’s Native Token
- Polkadot vs. Ethereum: Which Is A Better Deal?
- Is Polkadot Worth Investing In?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Polkadot
- Closing Thoughts
I provided the links of the details of each subheading for easy navigation while reading.
Now that we have the itinerary, let’s proceed into the Polkadot sphere.
1. What is Polkadot?

Polkadot is an open-source project that was founded by Gavin Wood, Peter Czaban, Robert Habermeier, and Web3 Foundation.
It was launched in May 2020 but has been in the pipeline since 2017 after its ICO.
The sole mission of Polkadot is, first, to create a web where users are wholly in charge of their data i.e it is free from any central authority.
Again, they will be able to send this data (no matter the type) across any type of blockchain.
To achieve this, it built a protocol that allows diverse blockchains to transfer messages and value in a secure way.
Secondly, Polkadot grants a common ground for other blockchains to interact with each other.
This is unlike conventional blockchains that can only interact with themselves,
That’s an overview of what Polkadot is about. You can find additional info here.
But you might ask: Why do we need Polkadot?
We already have Ethereum and other platforms that get the job done. So why create a similar thing?
Find the answer to this in the next subheading.
2. Why Do We Need Polkadot?
For some years, Ethereum was the only blockchain that allows other blockchains to create DApps on it.
Being the first and reliable, we saw the blockchain becoming overwhelmed with activities in no time.
This resulted in slower transaction confirmation; making scalability to be Ethereum’s Achilles heel.
With this came increased (no, scratch that) crazy gas fees.
You see a user being charged more than $90 for maybe a $35 transaction…..paying way higher fees than the transaction itself.
And again, there is nothing like blockchain interoperability – all chains run their own show.
Then came the likes of NEO, Cardano, EOS, and more recently Binance Smart Chain(BSC).
These platforms helped to serve the scalability issues to an extent but there’s still that part of chains interoperability.
BSC touched on this aspect but the bridge is just for the Binance Chain, its predecessor, and Ethereum (because it is EMV compatible).
But what of the other blockchains? Who interacts with them?
Then aboard came Polkadot, the mother of blockchains. Its mission is to make blockchain interaction possible.
This interoperability cuts across open, public, and permissionless blockchains as well as private, permissioned ones.
It does this by providing a Relay Chain (meaning in a later subheading) that hosts large verifiable data structures.
This can then be accessed by the various blockchains that need them.
It also ensures that the individual blockchains are secure and dealings with them are executed faithfully.
So it is very possible for you to use permissioned data gotten from a private blockchain on a public one.
Not just that, it also allows you to build your own blockchain and DApps on top of its protocol.
Furthermore, it gives you the opportunity to pick specific parameters to include in your design.
Blockchains can opt to keep their own validator set or choose to use Polkadot’s pooled security system to verify transactions through the Relay Chain.
On the Polkadot network, the features of a blockchain can be leveraged on another.
In a layman’s term, it’s more like the blockchain of blockchains … a one-stop-shop for developers!
Talk about convenience at its best!
This protocol came up quite aptly in this era when the topic of blockchain interoperability is becoming a thing.
With these added advantages, Polkadot becomes the succour for developers who wish to enjoy some extra services.
Next, we will see the stages of launch of the Polkadot project since its inception in 2017.
3. Polkadot Development Phases
As mentioned earlier, Polkadot finally launched in 2020 after being under development since 2017.
In this part, you will read about how far it has gone and the current phase it is in.
October 2017
The Polkadot project began with the release of its whitepaper in 2016. But it wasn’t until a year later that the project raised funds through an ICO.
10 million coins were set apart for the ICO and approximately 5 million coins were sold.
The first token sale ended on October 27, 2017, raising a total of 485,331ETH i.e more than $140 million.
In November 2017, there was an issue with the Parity wallet which led to the loss of more than 60% of the ICO funds.
The second and third token sales took place in 2019 and 2020 respectively.
May 2018
Polkadot’s Proof of Concept (POC-1) was released and it focused on the development of Relay Chains, the backbone of the Polkadot Network.
July 2018
At this point, owners of testnet DOT voted to approve a Referendum to update the testnet from POC-1 to POC-2.
This introduced the ability to develop parachains, staking rewards, etc.
January 2019
This saw the launch of testnet POC-3 which includes the GRANDPA (GHOST-based Recursive Ancestor Prefix Agreement) mechanism.
April 2019
POC-4 was launched and it brought with it new staking features.
This makes running a validator on Polkadot more secure and customizable.
August 2019
Kusama, an early unaudited version of Polkadot was released.
May 2020
The genesis block of Polkadot was launched as a Proof of Authority (POA) network.
Governance was then restricted to the single Sudo (super power) key which was held by Web3Foundation.
Later, validators began to join the network and indicating their interest to participate in consensus.
June 2020
Web3 Foundation, after ensuring that there are sufficient validators, initiated the validator’s election using its Sudo key.
By this act, Polkadot transitioned from Proof of Authority to Nominated proof of Stake.
July 2020
This saw the removal of Sudo and thus, handing Polkadot governance over to DOT holders.
August 2020
We had the redomination of DOT.
From August 21st 2020, 1 DOT = 100 new DOT tokens.
This change was voted for by the community of DOT holders.
Upcoming Updates
These include Core functionality and Polkadot 2.0.
Next in line of discussion is the technology of Polkadot – how does it do what it does?
Find out in the next section.
4. Polkadot Technology: An Insight On How It Works

Here, we will look at its Architecture, Consensus mechanisms, and Consensus roles.
a. Architecture
Polkadot’s architecture has these 4 components:
- Relay Chain
- Parachains
- Parathreads
- Bridges
Relay Chain
This is the heart of the Polkadot network. It sees to the network’s shared security, consensus, and cross-chain interoperability.
In short, its main responsibility is to coordinate the system as a whole including the parachains.
Parachains
These are individual blockchains that can have their own tokens and maximize their functionality for specific use cases.
They got their name from the concept of parallelized chains that run parallel to the Relay Chain.
Parathreads
Simply put, Parathreads are Parachains that don’t enjoy the full functionality of the network.
They are an idea for the Parachains to participate on a pay-as-you-go basis in the security of Polkadot.
This is done by sharing the scarce resource of a Parachain slot among the competing resources (Parathreads).
These are chains that cannot afford a full slot or maybe, do not deem it wise to do so.
Also meant for Parachains that no longer need a dedicated Parachain slot but still want to use the Relay Chain.
However, this is done with an associated fee per block.
Bridge
This component serves as the tool for blockchain interoperability on Polkadot.
It serves as the gateway for diverse blockchains to interact with each other.
There are different bridge designs ranging from centralized and trusted to decentralized and trustless bridges.
For Polkadot, its bridge design will is one that is decentralized and trustless.
Such a bridge can be built following any of these methods:
- smart contracts
- bridge pallets
- higher-order protocols
Find more information on this here.
b. Consensus Mechanism
Polkadot uses 2 consensus mechanisms – GRANDPA and BABE.
Let’s see their details below.
GRANDPA (GHOST-based Recursive Ancestor Deriving Prefix Agreement)
This mechanism was invented by Alistair Stelwart, a research scientist at Web3 Foundation.
He came about this concept while studying the Byzantine agreement protocols.
Polkadot settled for it because it tries to agree on the chain everybody agrees on (not just specific ones) not minding how many blocks it contains.
Read more on this here.
BABE (Blind Assignment for Blockchain Extension)
BABE mechanism is a block production mechanism that is similar to Ouroborous Praos but with some key differences.
It runs between validator nodes and determines the authors of new blocks
The mechanism can be used alone or with another, for example, GRANDPA.
Learn more about BABE here.
Let’s see the consensus roles and what each role has to do below.
c. Consensus Roles
There are 4 Consensus Roles and they include:
Nominators
They are users who secure the Relay Chain by selecting good validators and staking DOT.
As a nominator, you ought to pick good validators. Find out how to here.
If any of your selected Validators misbehave, they will get slashed and you will lose DOT as well.
But when they adhere to the rules of the network, you can get a share in the staking rewards that they generate.
Validators
A Validator maintains the Relay Chain by:
- staking DOT
- participating in consensus with other validators
- validating proofs from collators
For these functions performed, they get to earn staking rewards and from transaction fees.
For non-compliant validators, they suffer the removal of some/all of their staked DOT as punishment.
There are more than 600 validators on the Polkadot network with up to 64% of DOT staked (info as of 27th April 2021).
Collators
Parachains are maintained by Collators that work to:
- keep back all necessary info of the parachain
- maintain a full node of the parachain
- produce new block candidates for the Relay Chain validators
The collators will not continue building blocks on a parachain until the block candidate proposed to the Relay Chain validators has been approved.
Unlike Validators, Collators do not need to secure the network. This is because if a parachain block is invalid, it will get rejected by validators.
Fishermen
They can be said to be the guardians of the network.
They monitor the network and report bad behavior to validators.
A Collator or any Parachain full node can perform the role of a Fisherman.
To become one, an unspecified amount of DOT needs to be staked and can be slashed if the Fisherman submits an invalid report.
Note: Fishermen are not available on Polkadot yet. Update on this will be given by the team.
That’s it on Polkadot’s technology. Hope it was clear enough?
Next, we look at the governance token of the Polkadot network – DOT.
5. DOT – Polkadot’s Native Token
DOT is the native token of the Polkadot network. This is the same case with BNB for Binance Smart Chain and Ether for Ethereum.
Being a native token, it is used to do the following on the network:
- governance
- pay transaction fees
- parachain slot acquisition
- parathread bidding
- staking for consensus
The smallest unit of DOT is called a Planck; just like Bitcoin’s Satoshi or Ethereum’s Gwei.
As earlier mentioned in the phases section, DOT underwent a redenomination (change in the denomination) on the 21st of August 2020.
The purpose of this is to avoid the use of small decimals and thus, making calculation easier.

Before then, one DOT contained 1.000000000000 Planck. But after this date (21/08/2020), one DOT contains 100.000000000 Planck.
What this means is that a user that has 1.000000000000 Planck will still have the same number of Planck but will now have 100 DOTs under the new denomination.
DOT is an inflationary coin and the inflation rate is approximately 10% per year.
Part of the inflation is rewarded to validators for performing their duties while the rest may go directly to the treasury.
The exact percentage that goes into both varies and is based on the amount of DOT that is staked.
To get your hands on some DOTs, you have to buy from exchanges such as:
Wallets that support the storage of DOT are TrustWallet, PolkaWallet, Parity Signer, Ledger Wallets, Atomic wallet, etc.
As of 27th April 2021, the price of DOT is $34.31 with a market capitalization of $32,018,204,823.
It ranks as the #8 coin on CMC and has a circulating supply of 933,127,263 DOTs (the maximum supply is not specified as it is an inflationary coin).
That’s it on the DOT token. In the next section, I will compare the Polkadot network with the king of DApps platform – Ethereum.
Just scroll down.
6. Polkadot vs Ethereum: Which Is A Better Deal?
These platforms are similar in some ways. For example:
- they both support developers to build their projects on them
- they both have their native tokens which serve as the governance tokens
But though both platforms are somewhat alike, they still have many dissimilarities.
Find the differences in the table below.
| Parameters | Polkadot | Ethereum |
| Coin | DOT | ETH |
| Launch year | 2020 | 2015 |
| Founder | Gavin Wood | Vitalik Buterin |
| Rank on CMC | #8 | #2 |
| Price | $33.90 | $2,612.08 |
| Market Cap. | $32,018,204,823 | $300,599,740,491 |
| Circulating Supply | 933,127,263 DOT | 115,641,669 ETH |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Stake (GRANDPA and BABE) | Proof of Work (Ethash) |
| Fees | Weight-based model | Gas-metering model |
| Architecture | Multi-chain | Single chain |
| Programming Language | Rust C++ Etc. | Solidity |
| Transactions per second (tps) | >160,000 tps | 3000 tps |
| Block Time | 6 secs | 13 secs |
| Hosted Projects | 4 | 2,782 |
| Blockchain Interoperability | Yes | No |
Which is a better deal?
Making a choice here will solely depend on what the developer/user wants.
I mean they are both great platforms and blazing the trail with their different functionalities.
I think Ethereum is a better choice for you if you seek a tested and trusted platform where you can:
- easily create a smart contract
- do not need much control over the platform’s economics
- interaction within just the projects of the same ecosystem
But Polkadot does it for you if your focus is on:
- creating something that will require interchain operability
- being in full control of your project’s economics
- higher transaction throughput
That’s it on the comparison.
Guess you are still wondering if Polkadot is a worthy investment. Follow me to the next section to find out for yourself.
7. Is Polkadot Worth Investing In?
I will say YES, Polkadot is worth adding to your investment basket… will tell you why I said so in a jiffy.
Yes, it’s somewhat new and all but I believe it’s one for keeps.
For starters, Polkadot is coming as a worthy alternative to Ethereum.
I mean it gives the opportunity to do the same things as Ethereum and much more at a cheaper and faster rate.
So, what more can I ask for?
Polkadot’s main selling point is that it allows chains to interact with each other.
This singular functionality alone offers a developer legos, sort of, to add on when building.
Looking at the team behind it, we find a crypto pioneer championing its cause with the Web3 Foundation.
Gavin Wood has been involved in Ethereum creation and can be said to be one that has garnered enough knowledge and expertise in the crypto field.
Its DOT coin is not doing so badly after all.
Despite being relatively new, it has carved a name for itself as being among the 10 top coins on Coin Market Cap (as of April 2021).
This shows that it is on its way to the top of the list.
Considering its roadmap (which it has followed through) and the future plans it has, I believe Polkadot is on its way to making the crypto-sphere a better one.
But then, it’s just my opinion though; yours might run contrary to this.
Whatever your opinion, always remember the crypto-investment golden rule for every investment: Never invest more than you can afford to lose.
Above all, always do your own research on any project at all before investing.
Don’t worry, I am rounding up already… I will quickly go over some FAQs on Polkadot and we will wrap it up.
Let’s go and check out the questions.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Polkadot
If you can not find answers to your queries from the vast knowledgebase on its site, you can reach Polkadot’s team through the following channels:
– Twitter: https://twitter.com/polkadotnetwork
– Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/dot/
– YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCB7PbjuZLEba_znc7mEGNgw
– Discord: https://polkadot.network/assets/img/logos/logo-circle-discord.svg?v=eb01a431d7
– GitHub; https://github.com/paritytech/polkadot/
– Press inquiry: press@polkadot.network
– Read and contribute: https://wiki.polkadot.network/en/latest/
– Building on Polkadot: https://riot.im/app/#/room/#polkadot-watercooler:matrix.org
To make building on Polkadot easier for users, the team created a comprehensive guide on how you can do that on this page.
You can check it out to know where to start up.
Here’s an additional resource to further help you.
Kusama, as mentioned in the post, is an early unaudited version of Polkadot that was released in 2019.
Both networks share the same code thus they have the same architecture – multichain, on-chain upgrade, etc.
Again, governance on both platforms is decentralized and each user has a say once they hold their native tokens (DOT for Polkadot and KSM for Kusama).
Their key differences can be seen in the table below.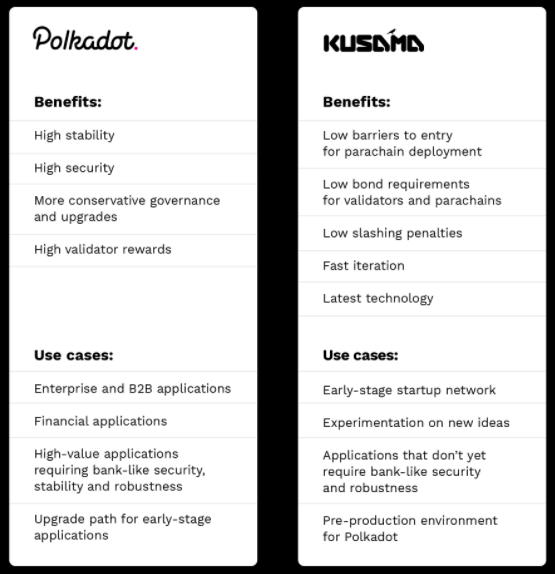
No, not all blockchains can be connected.
Polkadot can only connect blockchains that match these 2 criteria:
Criterion 1 – It must have the ability to form compact and fast light-client proofs over the finality and validity of its blocks and state change information.
Criterion 2 – There must be a means by which a large set of independent authorities (perhaps up to one thousand) can authorize a transaction.
Find out more info on this from the reply to this question ‘Can Polkadot connect any blockchain?‘ on this page.
If you want to learn how to trade cryptocurrencies profitably, we have created a perfect course to help you do that.
Enroll in our Cryptocurrency Mastery Course by going to www.ctmastery.com.
You can also join our Telegram community at https://t.me/ctmastery for more information.
9. Closing Thoughts
Here is the last section of today’s post. Hope you enjoyed reading through?
I took you on a journey into the Polkadot world making sure to point out all the vital points worth noting.
Guess you have some thing(s) to say now that we have moored into harbour.
So tell me: Do you use the Polkadot network? What has been your experience?
Do you think its DOT coin will ever flippen over ETH? Why do you say so?
If Ethereum eventually upgrades to Ethereum 2.0, do you think Polkadot will still be an Ethereum alternative?
Let me know what you think of these and your question (if any) by writing them in the comment box below.
It is said ‘Sharing is good, and with digital technology, sharing is easy! So true!
Just click on the share buttons below to help spread the Polkadot-news.



0 Comments