Aave is a ground-breaking protocol for lending in the DeFi Landscape.
Its token is currently (Feb 9, 2021) the no. 2 DeFi crypto in the list of “Top DeFi Tokens” by Coinmarketcap.
With over $4 billion worth of crypto locked in Aave, it becomes a very attractive space for cryptonites wishing to lend or borrow crypto assets.
In this post, you will get an in-depth review of just everything about Aave (with a major focus on Aave V2).
Ready to go? Let’s dive in.
Post Summary
What I will cover;
- What is Aave?
- Features of Aave
- How Does Aave Work?
- Supported Cryptocurrencies
- How to Borrow/Lend on Aave
- Aave Risk Framework
- Aave Vs Compound
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
Feel free to click on any of the links, if you are looking forward to learning from any of the specified items above.
What is Aave?

Aave is an open-source DeFi protocol for crypto lending and borrowing built on the ETH network.
It was launched by Stani Kulechou in 2017 as ETHLend – and was then, the first P2P money marketplace for lending and borrowing of crypto assets.
However, during the bear season in 2018, ETHLend suffered liquidity issues that it became difficult to match loan requests.
In a bid to restore the platform, the team at ETHLend rebranded to Aave and launched Aave V1 on Jan. 8 2020.
This saw Aave evolve from a P2P to becoming a full pool based protocol; providing expanded financial services than the former.
Moreover, Aave is a Finnish word meaning “ghost” in English, and it goes to imply that Aave is totally decentralized.
The launch of Aave came with full force and brought a lot of liquidity to the platform.
To ensure that the Aave ecosystem is running even more efficient, the team behind it launched AAVE V2 around Dec. 2020.
This is a total revamp of what Aave V1 offered.
Aave has become one of the most valuable DeFi projects currently on ground.
For the records, up to 24 ERC20 tokens are available for lending and borrowing, and over 4B worth of crypto are locked on the platform.
Aave Protocol requires no KYC, and the lending/borrowing processes are being carried out through a smart contract.
In the next section, I will lead you on to the features of Aave. Let’s dive in!
Features Of Aave
With the launch of V2, Aave now includes the following features;
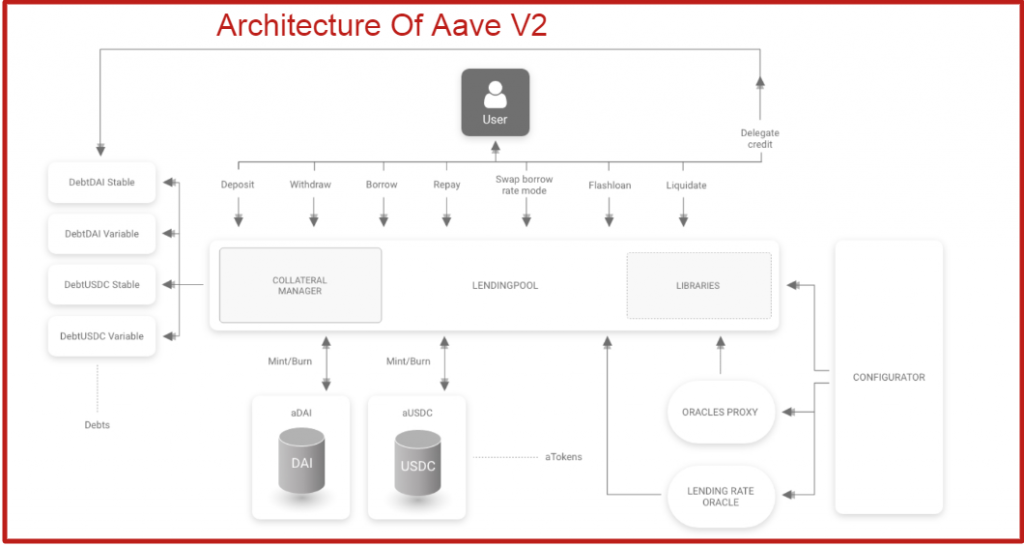
1. Collateral Trading
Aave V2 allows for the trading or the swapping of assets on the Aave network.
This feature primarily allows borrowers to avoid liquidation when their collateral starts to depreciate by trading their assets for a stable coin.
It equally gives the opportunity of swapping collateral into cryptos with a high yield at the moment.
2. aTokens
An aToken is issued when you deposit your asset on Aave and are also used for staking on Aave.
They are pegged 1:1 to the value of an underlying asset. For instance, you get aUSDT for depositing USDT on Aave.
More so, based on the example above, it is this your aUSDT that accrues interest in real-time directly in your wallet.
aTokens are burnt after a lender withdraws his asset from Aave.
3. Debt Tokenization
This token is issued to a borrower.
It is a debt accruing token that can be traded on a DEX. This is against the internal debt accounting which we have in Aave V1.
4. Gas Optimization
AaveV2 lowers the cost of transactions by up to 50% in some cases.
Also, a native Gas Token Support has been integrated, to help users reduce their transaction costs.
5. Stable and Variable Rate Borrowing
This is an interest rate that specifically applies to borrowers on Aave. I explained it in the next section
6. Credit Delegation
This allows lenders to lend their aTokens to borrowers to earn more interest.
It is also an opportunity for borrowers to obtain an uncollateralized loan from lenders.
The enforcement of the loan and its terms are agreed upon between the depositor and borrowers and not Aave.
Moreso, the agreement can either be made off-chain via legal agreements or on-chain via smart contracts.
7. Staking
This feature allows you to stake Aave tokens on the Aave pool.
8. Repayment with Collateral
This allows users to repay their loan using their deposited collateral unlike what we have in Aave V1 – where it is almost impossible to do so.
9. Batch Flash Loan
This was introduced against the flash loan in V1 that only allows users to borrow single crypto at a time.
With this feature made present, borrowers can now obtain a multi-crypto loan in one single loan.
Note: Some of these features are not available on Aave V1.
Do not worry, I will explain the difference between Aave V1 and V2 in the FAQ section.
Read through the next section!
How Does Aave Work?
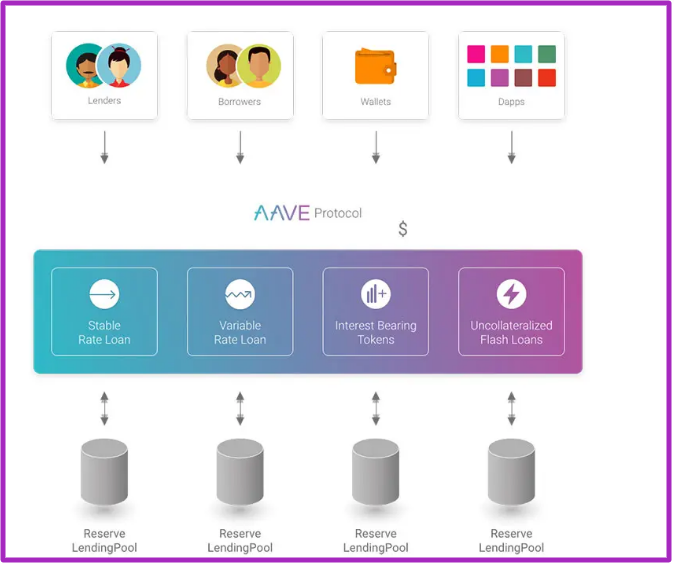
Cryptonites who wish to join any of the lending pools on AAVE can do so, by simply connecting their wallets to Aave.
Aave currently has 3 marketplaces;
- Aave V1
- Aave V2
- Uniswap (integrated into AAVE V1)
For this article, I will be focusing more on AAVE V2.
On Aave’s pool, lenders earn passively from borrowers interest rates by providing liquidity to the pool.
Borrowers, on the other hand, provide overcollateralized assets in ERC 20 tokens to gain access to loans in cryptos (on interest rate).
Interest accumulated are already displayed on each Aave’s network pool, and they differ from coin to coin.
- APY (Annual profit yield) for lenders
- APR (Annual profit return) for borrowers
The interest rate on Aave fluctuates based on market conditions.
For example, your interest rate becomes higher when you deposit or borrow a cryptocurrency that is in high demand on Aave at a particular time.
Also, the interest rate may get lower if there is no much demand for it by borrowers in the future.
However, in the case of a borrower, there is an option to choose between a variable or stable interest rate.
Variable interest rate – will rapidly fluctuate based on the market condition on Aave, just like in the example above.
Stable interest rate – is fixed for a short period of time but will follow the trend of the market condition in the long term.
Let’s have a look at the supported cryptos on Aave.
Supported Cryptos on Aave
Here you have them!
- DAI, USDC, TUSD, USDT, sUSD, BUSD, ETH,
- GUSD, AAVE, UNI, YFI, BAT, REN, ENJ, KNC,
- LINK, MANA, MKR, SNX, WBTC, ZRX, CRV
- xSUSHI, BAL, WETH
To further understand how AAVE works, let’s take a look at how to lend and borrow on Aave’s network pool.
See below!
How To Deposit and Borrow on Aave
How to Deposit on Aave
You can deposit your crypto assets on Aave either as a lender or borrower.
This is a step by step guide on how to deposit on Aave;
- Go to Aave, select the crypto you want to deposit, select a “Market place” and click on “Deposit”.
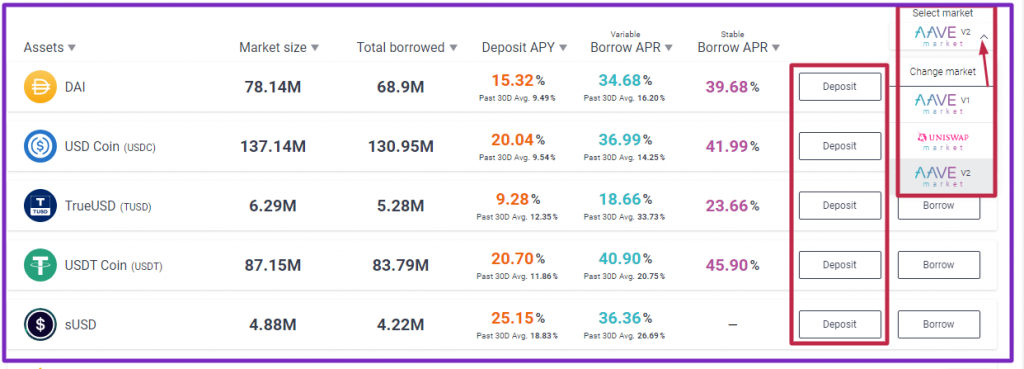
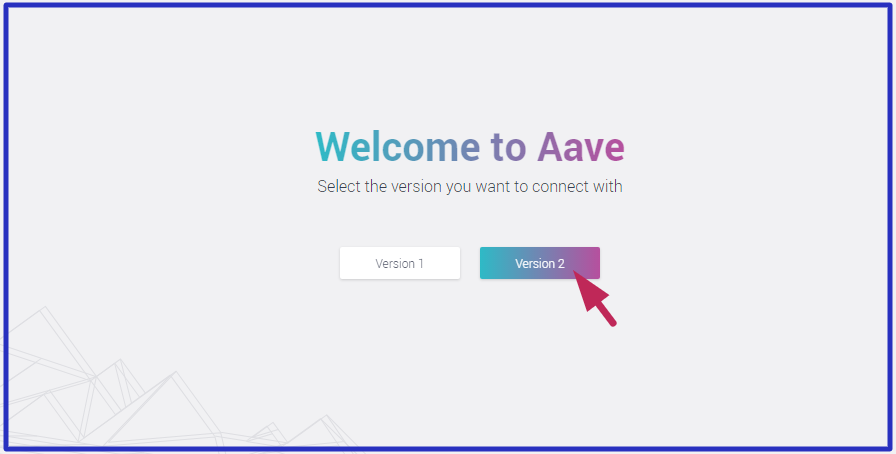
Note: Selecting from the first two marketplaces (as displayed on the screen) will direct you instantly to the Aave V1 URL to connect your wallet. However, Aave V2 will take you to the second step in this article.
- You will redirected to another interface, select Aave V2.
- Connect your web 3.0 wallet to Aave by selecting from the listed options.

For illustration: I will connect my MetaMask wallet to Aave by choosing “Browser Wallet” to complete the rest of the steps.

- Once you have connected your wallet, you will be redirected to Aave’s market place. Click on “Deposit” and proceed to deposit your asset into the Aave.
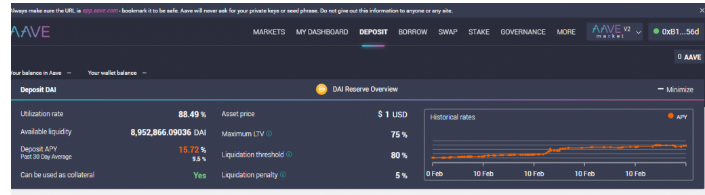
Let’s look at how to borrow!
How To Borrow on Aave
To borrow from Aave, here are the steps;
- Go to Aave, select the crypto you want to borrow, select a “Market place” and click on “Borrow”.
- Connect your Wallet to Aave (like we previously did).
- Click “Borrow” to obtain a loan on the asset you have selected.
- Set the amount of loan you want to collect, select your interest rate type( either “stable or variable”.
- You can always change your rate afterwards as many times as you want.
Note:
To borrow from Aave, you must deposit your collateral using the same deposit process in this article.
Let’s look at the parameters for issuing loans on Aave!
Aave Risk Framework
Each asset in the Aave protocol has specific values related to its risk. This influences how they are loaned and borrowed.
The table below gives a total rundown of the value placed on each crypto.
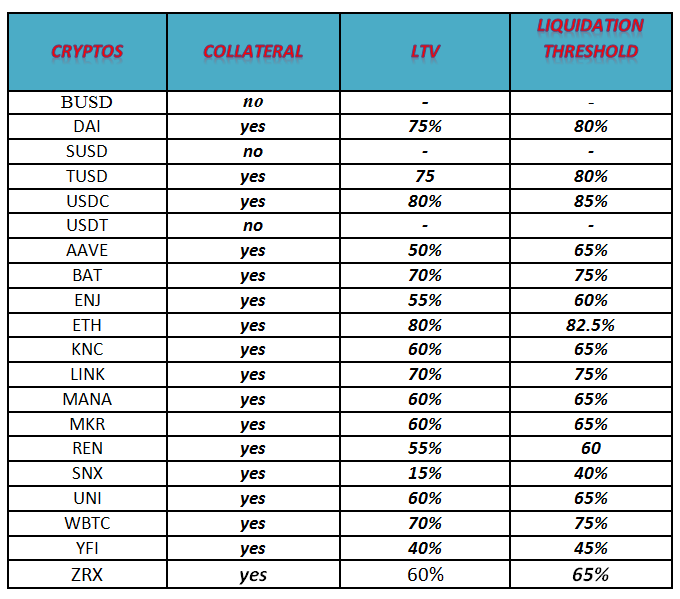
- Collateral: This shows if a crypto can be used as a collateral on Aave or not.
According to Aave,” tokens which risk exposure to single counter-parties cannot be used as collateral”.
- LTV: This simply stands for “Loan to value”. it represents the maximum amount of currency that can be borrowed with specific collateral.
For example: if you use DAI as collateral, the maximum amount of loan you will get must equal 75% of your DAI.
- Liquidation Threshold: This is the percentage at which your loan can be liquidated.
For example, a Liquidation threshold of 80% means that if the value rises above 80% of the collateral, the loan is under collateralized and could be liquidated.
Taking a deeper dive, let’s compare Aave with its rival Compound.
Aave Vs Compound

Compound was founded by Robert Leshner in 2018.
It is a lending protocol built as a smart contract in the ETH blockchain, just like Aave.
Compound and Aave are some of the popular protocols on DeFi. Although Aave token (AAVE) ranks higher than (COMP) on Coinmarketcap (Feb 9, 2021).
Both are similar in the sense that they offer overcollateralized loans to borrowers and equally have their native tokens (COMP, AAVE).
However, COMP is used as an incentive to reward both lenders and borrowers on its pool, this is not so with AAVE.
On Aave borrowers can switch their interest rate from “Variable to Stabe”; you can’t do that on Compound.
Again, Aave supports more crypto and offers a higher collateral percentage (75%) than Compound (66.6%).
When compared in terms of user-friendliness, Compound does not have all the sophisticated features and Aave, therefore, it is more user friendly.
Learn more about Compound here.
Now, let’s hit the FAQ section!
FAQs
The upgrade from Aave V1 to V2 brought so many changes to the protocol.
Some of these changes were light, while others are quite advanced.
For instance:
(i) Aave V1 will only give you an aToken when you make a deposit.
However, on Aave V2 you will also receive a token that accrues debt for borrowing on the protocol.
(ii) You can only choose between “stable and variable” interest rates on Aave V1 but Aave V2 allows you to flexibly switch between these two rates at any time.
I have written down the features of V2 in the second subheading of this article. However, if you want to learn more, visit here.
Flashloans are loans that do not require collateral but must be repaid within the same transaction.
You can learn more about Flashloan by clicking on this link.
Aave stated on the website that “You can migrate your positions from V1 to V2 without closing V1 manually”.
It also stated that a migration tool will be introduced and integrated into V1 UI for seamless and cost-effective migration. Read up.
Aave has tow types of fees are they are ;
* Borrower Fee (applicable to V1 alone): 0.00001%
*Flash Loan Fee: 0.09%
Note: There are also transaction fees for Ethereum Blockchain usage, which depend on the network status and transaction complexity.
P.S
Do you want to learn how to trade cryptocurrencies profitably?We developed a perfect course to help you master Cryptocurrency Trading.
Go to www.ctmastery.com to enrol.
Conclusion
Here comes the end of Aave review!
I believe you are now well-grounded about this DeFi protocol?
From my POV, Aave is really an attractive space that cryptonites can leverage on to make extra cash…Or what do you think?
What do you think about Aave space…Do you think it will keep blossoming in the future to attract more keen investors?
Have you joined the pool? Tell us about your experience so far.
Perhaps, you want to join because of what you have read here…
You can tell me all about it in the comment section.
In my next post, I will talk about Aave token (AAVE), hope to have you back soon!
Remember to share this article with your friends by clicking on the social media icons below. Cheers!
Related Articles;
- Akropolis Review – All You Need To Know About This DeFi Project
- What is Yield Farming? – What It Is and How It Works
- 0x(ZRX) Review 2020: Is It the Future of Decentralized Exchange?
- Steem – The Social Media Coin | The Most Complete Review (2020)
- TRON(TRX) Coin Review – Will The Value Appreciate in the Future?



0 Comments